Laser Surgery
LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis)
To treat abnormalities of refraction of small or moderate degree we also using eye operation - LASIK (Laser - Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) by an excimer laser of the last generation “Allegretto Wave”(Germany). LASIK stands for laser in situ keratomileusis, which means using a laser underneath a corneal flap (in situ) to reshape the cornea (keratomileusis). This procedure utilizes a highly specialized laser (excimer laser) designed to treat refractive errors, improve vision, and reduce or eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses. An ultra-thin flap is created on the eye's surface during LASIK corrective eye surgery. After laser energy is applied to reshape the eye, the flap is replaced to serve as a type of natural bandage. LASIK has advantages over other vision correction procedures, including a relative lack of pain afterward and the fact that good vision usually is achieved by the very next day. The surgeon uses a computer to adjust the excimer laser for your particular prescription.
Photorefractive keratotectomy (PRK)
Photorefractive keratectomy was the first method of vision correction using Excimer laser. PRK is a non-contact Excimer laser ablation of cornea surface layers, having no influence on the inner structures of the eye. The main purpose of this surgery is practically the same as in LASIK procedure – to improve vision by correcting abnormalities of refraction. As follows:
- Myopia (short or nearsightedness) from -1,0D to 6,0 D;
- Astigmatism from -0.5D to -3.0 D;
- Hyperopia (farsightedness) up to +3.0 D.
PRK and LASIK are basically the same technique, however there is a difference between them. In PRK procedure, epithelium is removed and the outermost layer below the epithelium is treated with laser. In LASIK, epithelium is not removed. The surgeon will fold the epithelial layer out of the laser treatment field, and fold it back in its original place after cornea has been reshaped by laser. PRK does not involve a knife, microtome or cutting laser as used in LASIK, but recovery period versus LASIK could lasts longer.
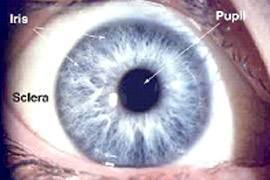 Laser trabeculoplasty (SLT)
Laser trabeculoplasty (SLT)
The new laser technique of Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty (SLT) allows decreasing intraocular pressure and compensating open-angle glaucoma in 1 - 2 procedures on an outpatient basis and it is easily tolerated by a patient.
YAG (Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) Laser dissection (discision) or capsulotomy
Because of some natural reasons, some of the patients who had cataract removal surgery with implantation of artificial intraocular lens (IOL) gradually developed posterior capsule opacification. It becomes cloudy, and this process is known as a secondary cataract.
The standard procedure for secondary cataracts is a form of laser cutting the capsule or YAG Laser dissection of secondary cataract. A simple laser surgery, called YAG laser posterior capsule dissection destroys cloudy posterior capsule from the optical axis, what helps to restore vision. The procedure is painless, does not require anesthesia and is accompanied by a low-risk, as it does not require cutting the eye.
Laser goniopuncture is a procedure performed using the Nd:YAG laser to improve aqueous outflow through Descemet’s window. Goniopuncture is indicated for glaucomatous patients who have undergone surgery, but whose intra ocular pressures (IOP) remains too high.
Gonipuncture may lower IOP without the need for a more invasive procedure. One or more openings are made in Descemet’s window with the laser, using a goniolens for visualization. As always, the intent is to lower intra ocular pressure.
Laser iridectomy (iridotomy) in angle-closure glaucoma
Laser iridectomy in angle-closure glaucoma, laser iridectomy is a surgical procedure that is performed on the eye to treat angle-closure glaucoma, a condition of increased intra-ocular pressure in the front (anterior) chamber of the eye that is caused by sudden (acute) or slowly progressive (chronic) blockage of the normal circulation of fluid within the eye.
Argon-laser iridoplasty (ALI)
Argon-laser iridoplasty is a safe and effective technique to improve visual function after multifocal IOL implantation to provide near distance vision in patients with small pupils. In cases of minimally decentered multifocal IOLs, argon laser iridoplasty can effectively improve vision. A surprising use for iridoplasty is to alter the pupil shape to reduce side-effects form decentered multifocal IOL’s.
Argon laser peripheral iridoplasty (ALPI) offers a new therapeutic option for primary angle closure glaucoma (PACG). The procedure consists of placing contraction burns in the iris periphery which results in contraction of the iris stroma and opening of the angle. 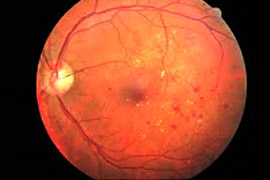 Barrage of the macular area
Barrage of the macular area
This is medical outpatient laser surgery, in which using laser coagulator applied dose of coagulants on the retina in order to reduce the swelling of various origins in the macular area.
Laser dissection of anterior synechiae
Anterior synechia causes closed angle glaucoma, which means that the iris closes the drainage way of aqueous humour which in turn raises the intraocular pressure.
Preventive peripheral laser coagulation of the retina (PPLC)
The laser surgeon could recommend to the patient to perform a preventive peripheral laser coagulation of retina ("laser welding"). The main idea of this treatment is based on the laser impact which results in sharp increase of the temperature and provokes coagulation of the tissue.
This easily tolerated out-patient procedure allows to consolidate the retina and to avoid spreading of the detachment to the central parts of the fundus. Due to this laser procedure many patients could avoid heavy eye operations.
The main purpose of preventive peripheral laser coagulation of the retina (PPLC) is to prevent retinal detachment and to decrease risks of complications, this type of laser treatment does not allow to improve vision.
Restrictive laser coagulation of the retina
Retinal laser coagulation is a minimally invasive procedure used to seal or destroy leaking blood vessels in the retina that lead to serious retinal conditions such as diabetic retinopathy and macular edema. This procedure can also seal retinal tears and destroy abnormal tissue found on the fundus.
Panretinal laser coagulation (PRLC)
Panretinal laser coagulation of the retina or laser photocoagulation is used to treat a number of eye diseases and has become widely used in recent decades. During this outpatient procedure, a special laser is used to make tiny burns that seal the retina and stop vessels from growing and leaking.
PRLC is used in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration, and having been proven to lower the risk of severe vision loss from these diseases. Also it is used to treat some other eye diseases including retinal ischemia, neovascularization of the choroid or retina.
Argon laser therapy of benign (non cancerous) eyelid’s tumors
Argon laser therapy of benign eyelid tumors may result in very satisfactory wound healing. It’s a useful alternative to traditional surgery, especially for tumors positioned close to the lachrymal papillae.
Argon-laser epilation of eyelashes
Trichiasis widely known as inturned eyelash refers to the condition where the eyelashes grow backwards and irritate the cornea of the eye. This condition leads to a feeling of a foreign body in the eye, which in turn causes severe symptoms of redness, pain, tearing, light sensitivity, and may lead to blindness.
In general, trachoma is the primary cause of trichiasis and is the leading infectious cause of blindness in the world. Lash misdirection in trachoma occurs secondary to involution of a normal lash line after posterior lamella scarring.
One of the methods we could offer to treat this condition is Argon laser epilation which allows to achieve a significant success with limited side effects because of precise tissue destruction. It is an appropriate choice when trouble some eyelashes are few and scattered, and when they are not secondary to an inflammatory condition. Side effects such as primarily short-lived edema and erythema are minimal comparing to more destructive conditions.
Laser stimulation of the retina
This method is based on the effect of the low intensity ray of light on eye structures. Low-energy laser stimulation has a positive effect on restoration of visual functions. This treatment results in improved microcirculation, metabolism and trophicity of the ocular tissues, activation of local immunity, and relaxation of the ciliary muscle. Laser stimulation is performed under local anesthetics as an outpatient procedure. Drops are placed in patient’s eye to dilate the pupils. The drops can take between 20-45 minutes to dilate your pupils fully. Laser beam is delivered using a slit lamp or microscope. A contact lens is placed on the eye and patient sits at a slit lamp. A patient feels a very bright light and a smaller red light. The bright light allows the doctor to see the internal structures of the eye and the red light is used for focusing. Various eye disorders could be treated by this method, one of them is diabetic macular edema. Laser stimulation of the retina in such cases is effective, safer, non-tssue harmful and cost effective treatment.
Laser stimulation of the cornea
Laser is very effective in the treatment of various conditions of the cornea. Low-intensity stimulation is used in multimodal treatment of corneal injuries such as perforating wounds, chemical and thermal burns, ulcers of various origins, and endothelial-epithelial dystrophy cases resulting from cataract extraction with implantation of IOL. A course of laser treatment usually consists of 6 to 10 daily 3 min exposures. The positive effect usually achieved by laser stimulation is significantly superior comparing with routine methods of treatment. He-Ne laser stimulation of the cornea is conducive to a sooner reduction of the inflammatory processes, to recovery of the corneal sensitivity and epithelialization, and to shortening hospital treatment.