Pediatric Ophtalmology
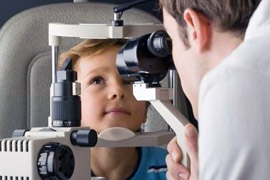 Visual acuity of a child changes with age. If eyesight of a child does not meet the age norms of pediatric ophthalmology, it is the absolute indication to undergo detailed examination of the pediatric ophthalmologist.
Visual acuity of a child changes with age. If eyesight of a child does not meet the age norms of pediatric ophthalmology, it is the absolute indication to undergo detailed examination of the pediatric ophthalmologist.
All reasons of decline of visual functions are divided into optical, that is associated with defects in the optical system of the eye (clouding of the cornea, lens, vitreous) or with abnormalities of the optical system of the eye (what includes congenital abnormalities of the eyeball), and the so-called sensory. The last one includes those which are associated with the violation of the perception of the light waves by the retina, a violation of the transmission of nerve impulses or pathology processing of visual signals to the brain.
Computer diagnostic
The medical mydriasis is caused by drugs instilled into the eye. Such as atropine, midriatsil, tropicamide, irifrin etc. Dilated pupils need for many ophthalmic examinations and some eye operations. More often medical mydriasis is used for detailed fundus examination. To prevent the spasm of accommodation (persistent muscle tension, leading to vision loss) doctors prescribe a course of cycloplegic - instillation within several days or weeks of eye drops, which relax the muscles of accommodation, while expanding the pupils.
Apparatus training of accommodation
A spasm of accommodation (or accommodative spasm) is a condition in which the ciliary muscle of the eye remains in a constant state of contraction. Normal accommodation allows the eye to "accommodate" for near-vision. However in a state of perpetual contraction, the ciliary muscle cannot relax when viewing distant objects. This causes vision to blur when attempting to view objects from a distance. This may cause pseudomyopia or latent hyperopia.
Although antimuscarinic drops can be applied topically to relax the muscle, this leaves the individual without any accommodation and, depending on refractive error, unable to see well at near distances. Also, excessive pupil dilation may occur as an unwanted side effect. This dilation may pose a problem since a larger pupil is less efficient at focusing light (see pupil, aperture, and defraction for more.)
Patients who have accommodative spasm may benefit from being given glasses or contacts that account for the problem or by using vision therapy techniques to regain control of the accommodative system.
Apparatus treatment of amblyopia ("lazy eye")
Amblyopia, commonly known as a “lazy eye”, is the eye condition noted by reduced vision not correctable by glasses or contact lenses and is not due to any eye disease. The brain, for some reason, does not fully acknowledge the images seen by the amblyopic eye. This almost always affects only one eye, but may manifest with reduction of vision in both eyes. It is estimated that about 3% of children under six have some form of ambliopia.
Orthoptics is the medical term for eye muscle training procedures. Technically, there are broad distinctions between Orthoptics and Vision Therapy (which includes Orthoptics). Orthoptics regards strabimus as an eye muscle problem and treatment is directed toward muscle strength.
Another problem is a pathology of the optic nerve and the retina.
The Division of Pediatric Ophthalmology of our clinic provides examinations, diagnosis, medical and surgical treatment of ocular, eye movement, and vision system disorders in neonates, infants, and children (at the age of 0-18 years old).
Eye conditions for this category of patients are as follows:
- Amblyopia (“Lazy eye”), a poor vision of one eye;
- Progressive myopia is an eye condition when abnormal length of eye ball may cause retinal vessels elongation, abnormal blood supply and visual acuity decrease;
- The process of myopia progression may be complicated by retinal tears, retinal detachment and decreased vision;
- Strabismus (Squint or cross-eyes), a condition in which eyes are out of line relative to one another, resulting in a permanent squint;
- Refractive errors, myopia (short or near sightedness), hyperopia (far or long sightedness);
- Astigmatism;
- Spasm of accommodation is a condition in which the ciliary muscle of the eye remains in a constant state of contraction and cannot relax. This condition causes blurred vision when attempting to view objects from a distance. This may cause pseudomyopia or latent hyperopia;
- Congenital and acquired or traumatic pediatric cataracts;
- Congenital pediatric glaucoma;
- Inflammatory, infectious and allergic eye diseases;
- Nystagmus, a condition of involuntary, usually side-to-side movements of the eyeballs that often accompanies other vision problems;
- Neuro-ophthalmic disorders;
- Retinopathy of prematurity, a degenerative condition of the retina;
- Eye and vision disorders associated with genetic diseases and diseases of metabolism, the nervous system, and the immune system.
Pediatric eye glasses prescription
In certain cases of progressive myopia in children we recommend individual means of myopia control – unloading bifocal spheroprismatic spectacles (BSPS). BSPS ensure a 4-fold reduction of visual loads at near distance. Special tests could help to detect potentially myopic young patients in time. Such children are prescribed BSPS that allow to avoid this condition at all. In cases when myopia has already appeared BSPS are prescribed to stop the process of vision deterioration. Our practice confirms high effectiveness of the method.

